1. Unsafe 介绍 1.1. 1、Unsafe 简介 Unsafe 类相当于是一个 java 语言中的后门类,提供了硬件级别的原子操作 ,所以在一些并发编程中被大量使用。jdk 已经作出说明,该类对程序员而言不是一个安全操作,在后续的 jdk 升级过程中,可能会禁用该类。所以这个类的使用是一把双刃剑,实际项目中谨慎使用,以免造成 jdk 升级不兼容问题。
1.2. 2、Unsafe Api 这里并不系统讲解 Unsafe 的所有功能,只介绍和接下来内容相关的操作
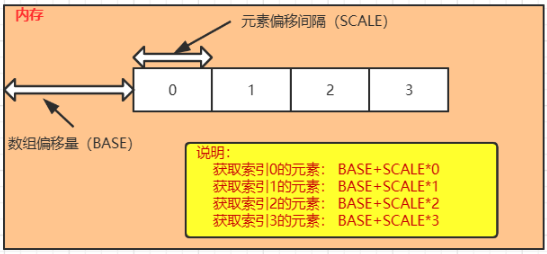
arrayBaseOffset:获取数组的基础偏移量
arrayIndexScale:获取数组中元素的偏移间隔,要获取对应所以的元素,将索引号和该值相乘,获得数组中指定角标元素的偏移量
getObjectVolatile:获取对象上的属性值或者数组中的元素
getObject:获取对象上的属性值或者数组中的元素,已过时
putOrderedObject:设置对象的属性值或者数组中某个角标的元素,更高效
putObjectVolatile:设置对象的属性值或者数组中某个角标的元素
putObject:设置对象的属性值或者数组中某个角标的元素,已过时
1.3. 3、代码演示 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 public class Test02 {public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception {2 ,5 ,1 ,8 ,10 };Unsafe unsafe = getUnsafe();int baseOffset = unsafe.arrayBaseOffset(Integer[].class);int indexScale = unsafe.arrayIndexScale(Integer[].class);Object o = unsafe.getObjectVolatile(arr, (2 * indexScale) + baseOffset);2 * indexScale) + baseOffset,100 );public static Unsafe getUnsafe () throws Exception {Field theUnsafe = Unsafe.class.getDeclaredField("theUnsafe" );true );return (Unsafe) theUnsafe.get(null );
2. 容器初始化 2.1. 1、源码分析 无参构造
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 public ConcurrentHashMap () { this (DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY, DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR, DEFAULT_CONCURRENCY_LEVEL);
三个参数的构造:一些非核心逻辑的代码已经省略
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 public ConcurrentHashMap (int initialCapacity, float loadFactor, int concurrencyLevel) { int sshift = 0 ; int ssize = 1 ; while (ssize < concurrencyLevel) { 1 ; this .segmentShift = 32 - sshift; this .segmentMask = ssize - 1 ; int c = initialCapacity / ssize; if (c * ssize < initialCapacity) int cap = MIN_SEGMENT_TABLE_CAPACITY; while (cap < c) 1 ; new Segment <K,V>(loadFactor, (int )(cap * loadFactor), new HashEntry [cap]); new Segment [ssize]; this .segments = ss;
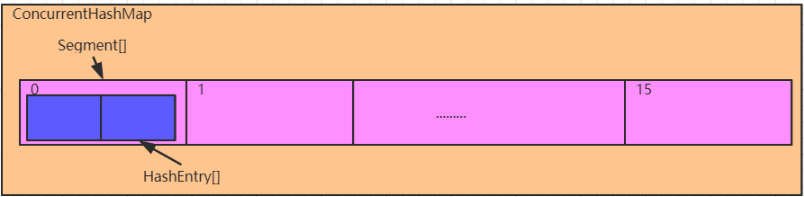
综上:ConcurrentHashMap 中保存了一个 **默认长度为 16 的 Segment[]**,每个 Segment 元素中保存了一个 **默认长度为 2 的 HashEntry[]**,我们添加的元素,是存入对应的 Segment 中的 HashEntry[] 中。所以 ConcurrentHashMap 中默认元素的长度是 32 个,而不是 16 个
2.2. 2、两个数组
2.2.1. Segment-extends ReentrantLock⭐️🔴 1 2 3 static final class Segment <K,V> extends ReentrantLock implements Serializable {
我们发现 Segment 是继承自 ReentrantLock 的,学过线程的兄弟都知道,它可以实现同步操作,从而保证多线程下的安全。因为每个 Segment 之间的锁互不影响,所以我们也将 ConcurrentHashMap 中的这种锁机制称之为 分段锁 ,这比 HashTable 的线程安全操作高效的多。
2.2.2. HashEntry 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 static final class HashEntry <K,V> { final int hash; final K key; volatile V value; volatile HashEntry<K,V> next; int hash, K key, V value, HashEntry<K,V> next) { this .hash = hash; this .key = key; this .value = value; this .next = next;
3. 添加安全⭐️🔴
3.1. ConcurrentHashMap 的 put 方法 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 public V put (K key, V value) { if (value == null ) throw new NullPointerException (); int hash = hash(key); int j = (hash >>> segmentShift) & segmentMask; if ((s = (Segment<K,V>)UNSAFE.getObject null ) return s.put(key, hash, value, false );
3.2. ConcurrentHashMap 的 ensureSegment 方法 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 private Segment<K,V> ensureSegment (int k) { final Segment<K,V>[] ss = this .segments; long u = (k << SSHIFT) + SBASE; if ((seg = (Segment<K,V>)UNSAFE.getObjectVolatile(ss, u)) == null ) { 0 ]; int cap = proto.table.length; float lf = proto.loadFactor; int threshold = (int )(cap * lf); new HashEntry [cap]; if ((seg = (Segment<K,V>)UNSAFE.getObjectVolatile(ss, u)) null ) { new Segment <K,V>(lf, threshold, tab); while ((seg = (Segment<K,V>)UNSAFE.getObjectVolatile(ss, u)) null ) { if (UNSAFE.compareAndSwapObject(ss, u, null , seg = s)) break ; return seg;
3.3. Segment 的 put 方法 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 final V put (K key, int hash, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent) { null : try { int index = (tab.length - 1 ) & hash; for (HashEntry<K,V> e = first;;) { if (e != null ) { if ((k = e.key) == key || if (!onlyIfAbsent) { break ; else { if (node != null ) else new HashEntry <K,V>(hash, key, value, first); int c = count + 1 ; if (c > threshold && tab.length < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) else null ; break ; finally { return oldValue;
3.4. Segment 的 scanAndLockForPut 方法 该方法在线程没有获取到锁的情况下,去完成 HashEntry 对象的创建,提升效率
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 private HashEntry<K,V> scanAndLockForPut (K key, int hash, V value) { this , hash); null ; int retries = -1 ; while (!tryLock()) { if (retries < 0 ) { if (e == null ) { if (node == null ) new HashEntry <K,V>(hash, key, value, null ); 0 ; else if (key.equals(e.key)) 0 ; else else if (++retries > MAX_SCAN_RETRIES) { break ; else if ((retries & 1 ) == 0 && this , hash)) != first) { 1 ; return node;
3.5. 模拟多线程的代码流程 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception { final ConcurrentHashMap chm = new ConcurrentHashMap (); new Thread (){ @Override public void run () { "通话" ,"11" ); "-----------" ); 1000 ); new Thread (){ @Override public void run () { "重地" ,"22" ); "===========" );
3.5.1. 流程图 https://www.processon.com/view/link/636a079b1efad40cd880e4fc
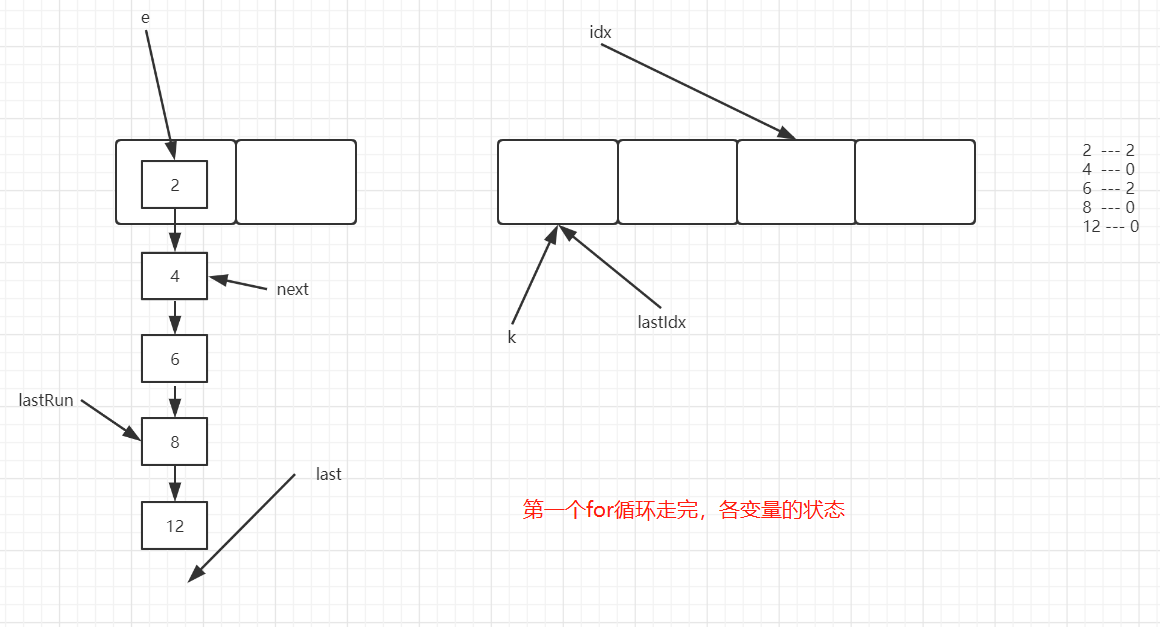
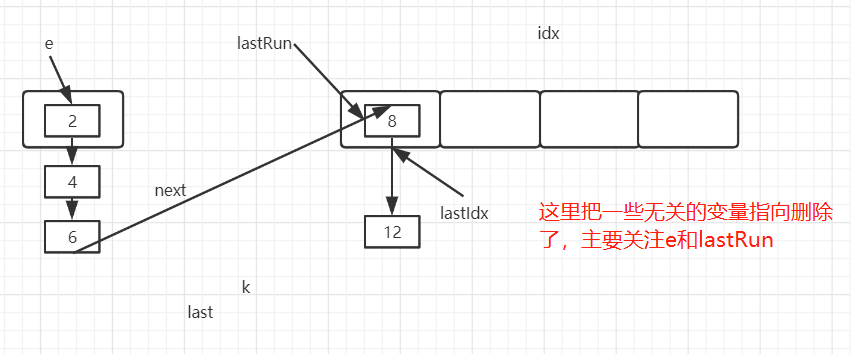
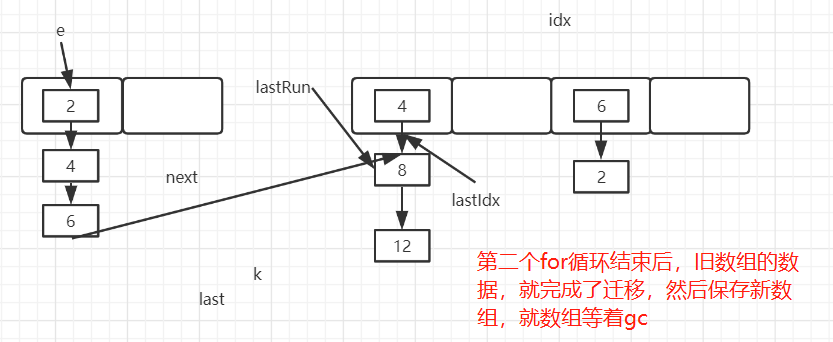
4. 扩容安全 4.1. 源码分析 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 private void rehash (HashEntry<K,V> node) { int oldCapacity = oldTable.length; int newCapacity = oldCapacity << 1 ; int )(newCapacity * loadFactor); new HashEntry [newCapacity]; int sizeMask = newCapacity - 1 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < oldCapacity ; i++) { if (e != null ) { int idx = e.hash & sizeMask; if (next == null ) else { int lastIdx = idx; for (HashEntry<K,V> last = next; null ; int k = last.hash & sizeMask; if (k != lastIdx) { for (HashEntry<K,V> p = e; p != lastRun; p = p.next) { V v = p.value; int h = p.hash; int k = h & sizeMask; new HashEntry <K,V>(h, p.key, v, n); int nodeIndex = node.hash & sizeMask;
既有串片段的重定向到新数组,也有复制元素到新数组
图一
图二
图三
5. 集合长度获取 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 public int size () { final Segment<K,V>[] segments = this .segments; int size; boolean overflow; long sum; long last = 0L ; int retries = -1 ; try { for (;;) { if (retries++ == RETRIES_BEFORE_LOCK) { for (int j = 0 ; j < segments.length; ++j) 0L ; 0 ; false ; for (int j = 0 ; j < segments.length; ++j) { if (seg != null ) { int c = seg.count; if (c < 0 || (size += c) < 0 ) true ; if (sum == last) break ; finally { if (retries > RETRIES_BEFORE_LOCK) { for (int j = 0 ; j < segments.length; ++j) return overflow ? Integer.MAX_VALUE : size;
6. 参考 https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV17i4y1x71z/?from=search&seid=3516507855592185473&spm_id_from=333.337.0.0&vd_source=c5b2d0d7bc377c0c35dbc251d95cf204