1. 队列
队列:是一个 有序列表,可以用 数组 或 链表 实现。
特点:遵循 先入先出 原则。队尾入队,队头出队。即:先存入的数据,先取出。
2. 假溢出
系统作为队列用的存储区还没有满,但队列却发生了溢出,我们把这种现象称为”假溢出”。
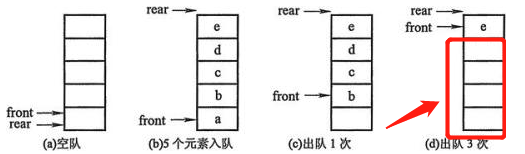
因为队列遵从从队尾存入数据,从队头取数据,所以红框部分的空间就不能继续存入新的数据,此时队列有多余的空间,却不能存入值,这种现象就叫做假溢出现象。数组中元素已出队位置需要循环利用。
3. 如何循环
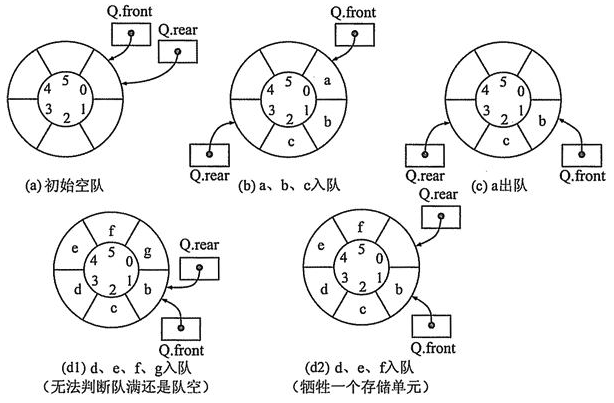
rear 指向队列尾的实际位置的后一个位置。并且rear和front的初始值均为0
而且默认希望空出一个空间不能存放数据,是因为如果不空闲空间,那么队列满和队列为空的条件会发生表意冲突(如上图中图a和图d1,rear和front在初始和队满时都会同时处在一个位置),为了区分,rear指向最后一个元素的后一个位置,利用取模巧妙表达队满时的位置状态。因此队列满的条件应该如下:
队列满: (rear + 1) % maxSize == front
队列空: rear == front
队列中有效数据的个数是:( rear + maxSize - front ) % maxSize
该算法取巧的地方在于 rear 的位置,注意看上图,rear 所在的位置 **永远是空的**,实现环形队列的算法也有多种,这里空出来一个位置,是这里算法的核心
4. 代码实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
| import java.util.Scanner;
public class CircleQueueDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
CircleQueue queue = new CircleQueue(3);
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
boolean loop = true;
char key = ' ';
System.out.println("s(show): 显示队列");
System.out.println("e(exit): 退出程序");
System.out.println("a(add): 添加数据到队列");
System.out.println("g(get): 从队列取出数据");
System.out.println("h(head): 查看队列头的数据");
System.out.println("t(tail): 查看队列尾的数据");
System.out.println("p(isEmpty): 队列是否为空");
while (loop) {
key = scanner.next().charAt(0);
switch (key) {
case 's':
queue.show();
break;
case 'e':
loop = false;
break;
case 'a':
System.out.println("请输入要添加到队列的整数:");
int value = scanner.nextInt();
queue.add(value);
break;
case 'g':
try {
int res = queue.get();
System.out.printf("取出的数据是:%d\n", res);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
break;
case 'h':
try {
int res = queue.head();
System.out.printf("队首数据:%d\n", res);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
break;
case 't':
try {
int res = queue.tail();
System.out.printf("队尾数据:%d\n", res);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
break;
case 'p':
System.out.printf("队列是否为空:%s", queue.isEmpty());
break;
}
}
}
}
class CircleQueue {
private int maxSize;
private int front;
private int rear;
private int arr[];
public CircleQueue(int arrMaxSize) {
maxSize = arrMaxSize + 1;
arr = new int[maxSize];
front = 0;
rear = 0;
}
public int get() {
if (isEmpty()) {
throw new RuntimeException("队列空");
}
int value = arr[front];
front = (front + 1) % maxSize;
return value;
}
public void add(int n) {
if (isFull()) {
System.out.println("队列已满");
return;
}
arr[rear] = n;
rear = (rear + 1) % maxSize;
}
public void show() {
if (isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("队列为空");
return;
}
for (int i = front; i < front + size(); i++) {
int index = i % maxSize;
System.out.printf("arr[%d] = %d \n", index, arr[index]);
}
}
public int head() {
if (isEmpty()) {
throw new RuntimeException("队列空");
}
return arr[front];
}
public int tail() {
if (isEmpty()) {
throw new RuntimeException("队列空");
}
return rear - 1 < 0 ? arr[maxSize - 1] : arr[rear - 1];
}
private boolean isFull() {
return (rear + 1) % maxSize == front;
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return rear == front;
}
public int size() {
return (rear + maxSize - front) % maxSize;
}
}
|
5. size大小计算
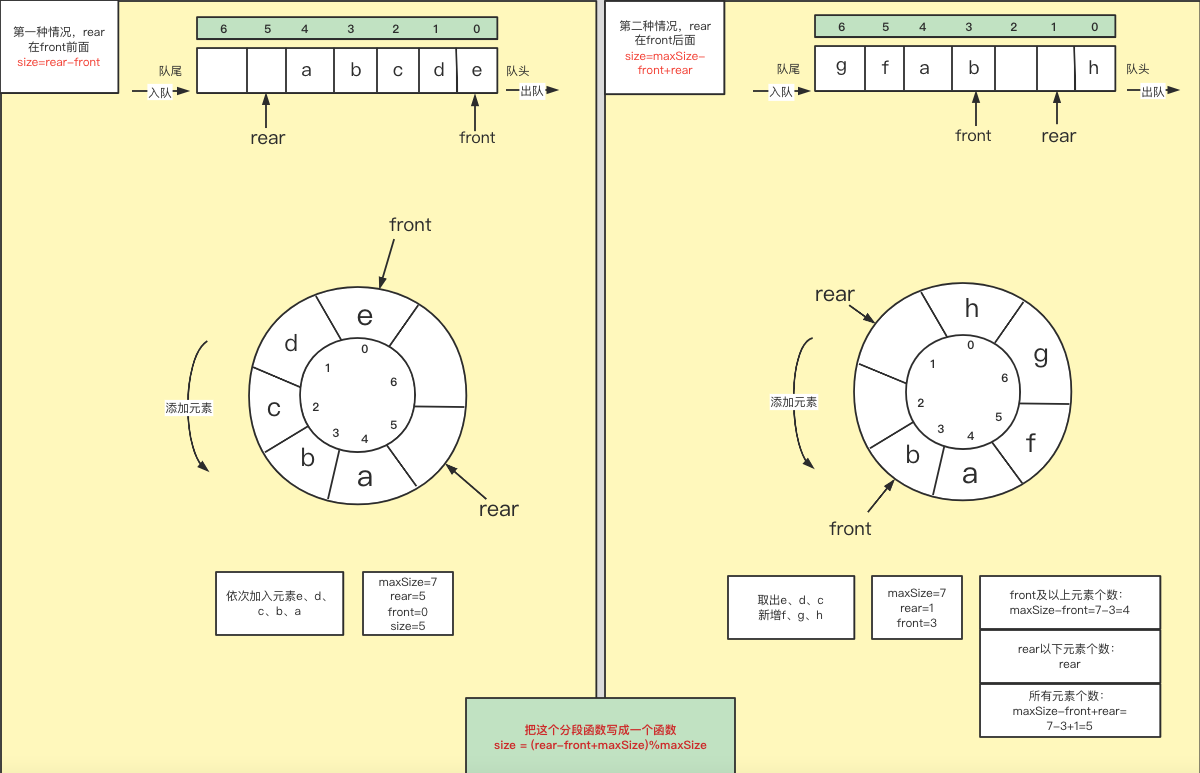
原图地址:https://www.processon.com/view/6332980c07912955b209c0d4?fromnew=1
6. 参考
https://www.cnblogs.com/yxm2020/p/12753564.html
https://zq99299.github.io/dsalg-tutorial/dsalg-java-hsp/03/02.html#%E4%BB%A3%E7%A0%81%E5%AE%9E%E7%8E%B0





